| University | National University of Singapore (NUS) |
| Subject | Economics |
Problem Set 1 (Algebra)
- What will a deposit of $4,500 at 7% compounded yearly interest be worth if left in the bank for 9 years? Show your calculations.
- How much money would you need to deposit today at 12% annual interest compounded yearly to have $1,000 in the account after 2 years? Show your calculations.
- How much interest will you earn after a year and what will be the value of your investment? How much total interest will you earn if you get 3% interest at the end of the 1st half of the year and at the end of the 2nd half of the year you receive 3% again on the capital plus the interest of the first half-year. In this case, what will be the value of your investment after a year? Show your calculations.
Problem Set 2 (Calculus and Excel)
Vanilla Inc. is an appliance manufacturer. Just recently, it invented a new hairdryer for pets (HDFP). The monthly demand and cost function for the HDFP product is as follows:
P = $60 – $0.005Q
C(Q) = $100,000 + $5Q + $0.0005Q²
- Create a table for the output (Q), price (P), total revenue (R), total cost (C), marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and profit (Π) functions in the range for Q from 0 to 10,000 in increments of 1,000.
- Create a graph in Excel for the revenue function (R), the cost function (c), and profit function (Π) with Q on the horizontal axis (independent variable). At what price/quantity combination is profit maximized? Why?
- Determine the profit-maximizing price/output combinations analytically (MR=MC and solve for Q). Show your calculations.
Buy Custom Answer of This Assessment & Raise Your Grades
Problem Set 3 (Game Theory)
Consider a small town with a population of dedicated pizza eaters but able to accommodate only two pizza shops, Maria’s and Alfredo’s. Each seller has to choose a price for its pizza. For simplicity, suppose for now that only two prices are available: medium and high. If a medium price is set, the sellers can achieve a profit margin of €10 per pie. The high price yields a profit margin of €12 per pie. Assume that there is a floating demand of 10,000 pies per week, no matter what price is charged in either store.
If both stores are charging the same price, this demand will be split equally between them. However, most of the people who buy these pies are price-conscious and will go to the store at a lower price. Let 80% of the people be price-conscious so they will go to the lower-priced store if prices between stores differ; 20% of the people don’t care and buy at the higher-priced store.
| Alfredo’s Pizza | |||
| Maria’s | High | Medium | |
| Pizza | High | 60,60 | 24,80 |
| Medium | 80,24 | 50,50 |
The above table shows the profits per week going to each pizza seller for thousands of Euros. To see where the profit values come from in each cell, consider the sample situation when Maria’s chooses a medium price and Alfredo’s chooses a high price. In that case, Maria’s will get 80% of the total (and floating) demand because of her lower price. Thus Maria’s sells a total of 8,000 pies and makes a profit of €10 per pie, yielding a profit per week of €80,000. (Because we are denoting profit levels in thousands in the table, the €80,000 profit for Maria’s becomes “80”). Alfredo’s gets to serve only 20% of the customers but at a higher profit margin of €12 per pie. His total profit per week is then €24,000 (“24” in the table). Similar calculations yield the numbers for the rest of the table:
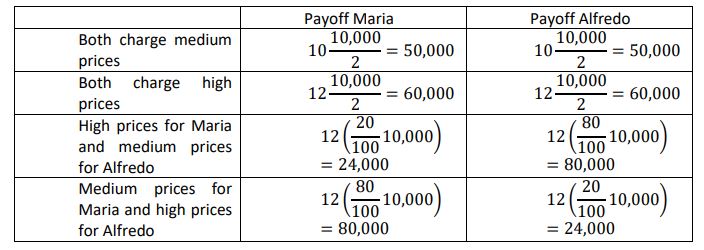
- Determine the most likely outcome if Alfredo and Maria only compete in the very next period and not in any period thereafter. Assume that both have to decide precisely now, without being able to communicate with each other. What is the insight from this game?
- What if Alfredo and Maria could advertise by distributing leaflets? Leaflets cost €10,000 to produce and distribute at a certain, meaningful number. Assume that Alfredo has a loyal captive customer base of 3,000 customers. If he advertises and Maria doesn’t, he gets 1,000 additional customers; if Maria also advertises, he only gets 200. Maria, unfortunately, has no loyal customers yet but she gets 2,500 new customers if she advertises and Alfredo doesn’t. If Alfredo does advertise, she gets 1,000. Any remaining floating demand is shared equally. Assume that pizzas can only be sold at the medium price of €10. Write down the profits table. As before, determine the most likely market outcome if Alfredo and Maria only compete in the very next period and not in any period thereafter and make simultaneous and uncoordinated decisions now.
Problem Set 4 (Tableau)
Download the TopBabyNames.xlsx from Moodle (Section: Class Lecture) and import it into Tableau. The file has five columns
- State: The U.S. state abbreviation
- Gender: M/F
- Year: Number
- Top Name: Baby name
- Occurrences: Number. How often the baby name occurred in a particular year in the specific state for the specific gender.
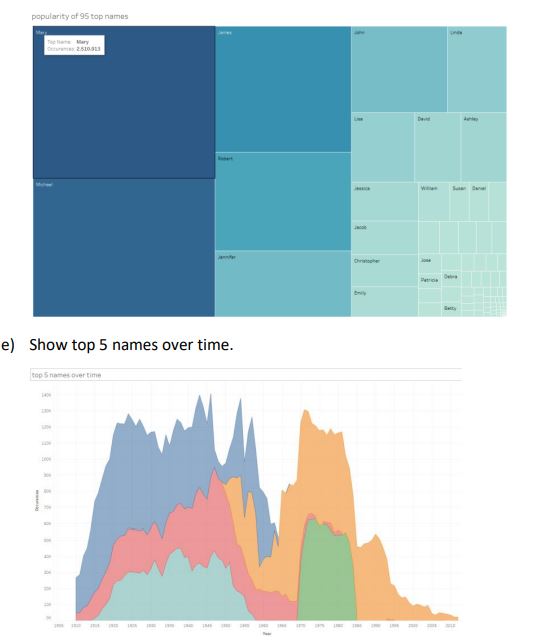
Perform the following analyses and design the visualization similar to the reference pictures below:
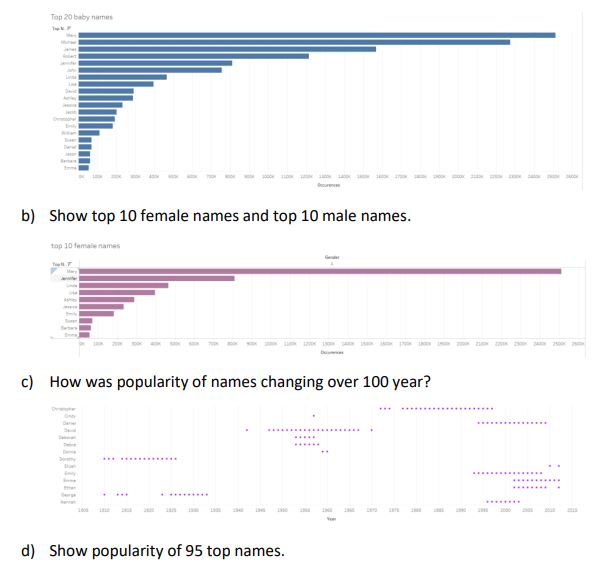
a) What are the top 20 names used in the USA for babies from 1910 to 2012?
If you are looking for help in your economics assignment then you have got the right website. Our expert writers are fully aware of its concepts and fundamentals hence they prepare good quality economics homework for you.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- INDIVIDUAL RESEARCH PROJECT: MERGERS AND THEIR IMPACT
- PSS388 End of Course Assessment January Semester 2025 SUSS : Integrated Public Safety And Security Management
- PSY205 Tutor-Marked Assignment 02 SUSS January 2025 : Social Psychology
- Math255 S1 Assignment-2025 SUSS : Mathematics for Computing
- BUS100 Tutor-Marked Assignment January 2025 SUSS : Business Skills And Management
- CSCXXX SUSS : New System Development Using Java : Soft Dev Pte Ltd Project
- Cloud Computing: Fundamentals, Networking, and Advanced Concepts
- COS364 Tutor-Marked Assignment January 2025 Sem SUSS : Interventions for At-Risk Youth
- FMT309 Tutor-Marked Assignment 01 SUSS January 2025 : Building Diagnostics
- HBC203 Tutor-Marked Assignment 01 January 2025 SUSS : Statistics and Data Analysis for the Social and Behavioural Sciences

