| University | RMIT University (RMIT) |
| Subject | Supply Chain Analytics Case Study |
Introduction
Considerable research during the last two decades has concentrated on aggregate production planning, inventory control, and scheduling. Aggregate planning procedures, which have been proposed for both manufacturing and service organizations, help determine monthly (or quarterly) output, inventory, and manpower aggregates.
Inventory and scheduling procedures, using the aggregate decisions as input, tend to focus on such short–term decisions as (i) the sizing and timing of production (purchase) orders for specific items, (ii) sequencing of individual jobs (orders), and (iii) short–term allocations of resources to individual activities and operations. The total process of going from aggregate plans to more detailed plans can be called disaggregation.
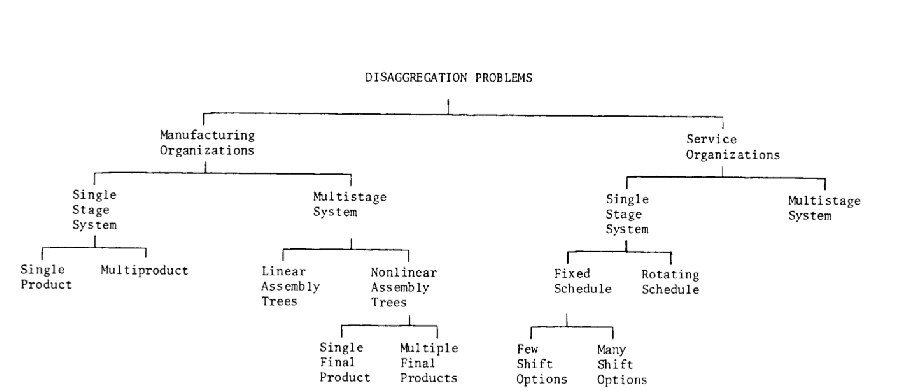
Depending upon the nature of the production system, disaggregation decisions in a manufacturing organization may exist on one or more of the following three levels:
1. Given aggregate decisions on output and capacity, determine the timing and sizing of specific final product production quantities over the time horizon (sometimes referred to as a master schedule).
2. Given the timing and sizing of final product production quantities, determine the timing and sizing of manufactured (or purchased) component quantities.
Stuck with a lot of homework assignments and feeling stressed ? Take professional academic assistance & Get 100% Plagiarism free papers
The taxonomy shown on the left side of Figure 1 provides the framework with which the three levels of disaggregation in manufacturing organizations.
Disaggregation problems in service organizations possess the complicating characteristics of stringent response time requirements, time-dependent demand rates, and no finished goods inventories to smooth production rates. Disaggregation decisions in service organizations also exist at three levels:
1. Given aggregate decisions on output and capacity, allocate manpower and other resources to specific operations over the time horizon (sometimes referred to as the staff sizing problem).
2. Given the allocation of resources to specific operations, determine the shift schedules and crew assignments of employees.
3. Given the shift schedule assignments, determine short-term adaptations, reallocations between operations, and priorities of the service requirements.
The right half of Figure 1 provides a basis for describing disaggregation problems in service organizations. Native Singapore Writers Team
Hire a Professional Essay & Assignment Writer for completing your Academic Assessments
For a transformative academic journey at RMIT University (RMIT), avail our specialized support in TMA and navigate the complexities of your Supply Chain Analytics Case Study with our dedicated case study assignment help online. Elevate your academic performance with our trusted assignment writing service in Singapore.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- HRM331: Talent Management – Strategic Shift from the War for Talent to the Wealth of Talent
- Marginalised Populations – The Structural and Cultural Exclusion of People Experiencing Homelessness in Singapore
- CVEN3501 Assignment 2: Groundwater Modelling of Drawdown from a Pumping Bore
- CSCI312 Assignment 2: Conceptual Modelling and Implementation of a Data Warehouse and Hive Queries
- CH2123 Assignnment : Fugacity, VLE Modeling & Henry’s Law Applications
- BAFI1045 Assignment -Constructing and Evaluating Passive and Active Portfolios Based on the Straits Times Index (STI)
- PSB501EN Assignment 1: Engineering Systems Integration: A Multi-Technique Approach to Mechanical Analysis
- FIN2210E/FIN2212E Group Assignment: Financial Risk Management Analysis of Bursa Malaysia Companies
- FLM101 Assignment: A Cinematic Dissection: Stylistic Elements and Their Thematic Significance
- Assignment: Transforming Talent in the AI Era: From War to Wealth through Ecosystem Innovation

