| University | National University of Singapore (NUS) |
| Subject | Macroeconomics |
Question 1:
(a) Differentiate between the development of the Global Financial Crisis and the Great Depression. Discuss how the different government policy approaches contributed to the length and severity of each event.
(b) Consider the impact of the COVID-19 crisis on economies around the world and assume our economy began the period at its natural rate of output.
- Using the Phillips Curve analysis, illustrate the impact of the crisis, identifying its new position as point A.
- As a result of the crisis, would the output ratio for this economy be equal to 100%, above 100% or below 100%?
- Explain how this economy will automatically return to its long-run position at the natural rate of output.
- If the government’s policy focus is on stabilization, rather than waiting for automatic adjustment, what action would it undertake and how would this be illustrated on the Phillips Curve?
- Discuss how the crisis could also impact on the supply side of the economy. If this happens, what will be the impact on the Phillips curve? What can the government do to return the economy to its natural rate? What is the consequence of this policy action?
Question 2:
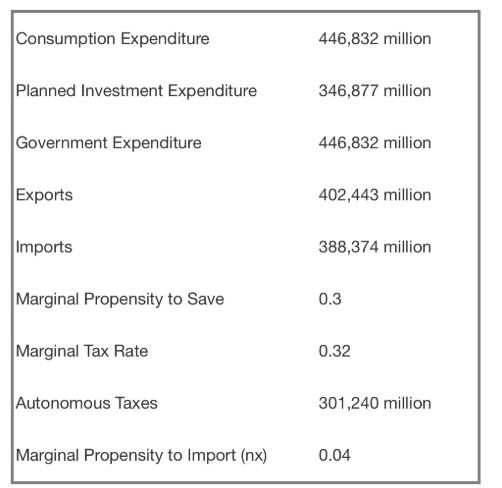
(a) Calculate the equilibrium level of income.
(b) Calculate autonomous consumption.
(c) Calculate autonomous net exports.
(d) Calculate autonomous planned expenditures.
(e) Calculate the marginal leakage rate.
(f) Assume that the natural rate of output for this economy is estimated at $1,200,000 million.
Stuck with a lot of homework assignments and feeling stressed ? Take professional academic assistance & Get 100% Plagiarism free papers
Question 3:
(a) Differentiate between financial intermediaries and financial markets.
- Imagine you are considering placing your savings into either a DBS Bank savings account or buying shares in Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd or purchasing Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd bonds, which of the three is the riskier option? Explain why.
- If you believe that interest rates in the economy are going to fall, where would you move your money – financial intermediaries or financial market? Explain why?
(b) If the stock of high-powered money in the economy is $117.2 billion; the reserve ratio is 12% and the fraction of deposits held as a currency is 5%, calculate
- the size of the money multiplier (provide an answer to two decimal points).
- the money supply (provide answers to two decimal points).
(c) Identify and illustrate the two components of money demand. Explain in detail the reasoning behind the slopes (shape) of the two components of money demand.
(d) Using the money market, illustrate what happens if income in the economy decreases.
- Assume the central bank responds to the decrease in economic activity by undertaking expansionary policy. Illustrate the impact on the money market.
- Explain how the expansionary policy in part (i) should transmit into the product market and boost economic activity.
- If the domestic economy slides into a recession as a result of the COVID-19 crisis, will the above policy action work? Why? Why not? Explain in detail.
Question 4:
(a) Assume that the economy is in equilibrium, but that equilibrium is associated with the actual level of output in the economy, well below the natural level of output.
- Describe the action that would be undertaken by the government to move the economy to the natural level of output.
- Using the IS-LM model, illustrate the impact of the policy (from part 1 above). Clearly identify the new equilibrium position on your diagram.
- Discuss in detail the costs of implementing the policy undertaken in part (i) above.
- If the central bank decides not to accommodate the policy undertake in part (i) above because it considers that the policy will breach its inflation target, what action will it undertake? Illustrate how this action will now impact the economy using the IS-LM model — include in the diagram both the initial government action undertaken, labeling the equilibrium as point A as well as the central bank policy outcome, labeling it as point B.
- Explain why a relatively flat IS curve and a relatively steep LM curve will reduce the effectiveness of the fiscal policy implemented above.
(b) Discuss the problem of adhering to the “Taylor” rule targeting inflation if severe supply shocks occur in an economy.
- Is this economy facing a recessionary or inflationary gap?
- Illustrate the gap you identified in part (i) above using both the AS-AD Model and the Aggregate Expenditure Model.
- Calculate the output ratio for this economy
- If the government wishes to move the economy to its natural rate, will it need to increase or decrease spending? Calculate by how much it will need to change its spending
- Consider the policy action undertaken in part (iv) above and illustrate the impact on the money market.
- Given the impact on the money market determined in part (v) above, explain how this could affect the exchange rate market.
- Explain the policy action the government could undertake if it decides that it wants to move the economy to its natural rate but doesn’t want the action to affect its budget position.
Question 5:
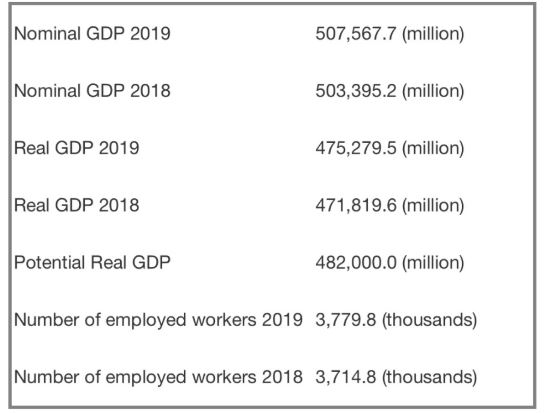
(a) Calculate the inflation rate over the period. If the base year in this economy is 2017, what is the inflation rate calculated as of the base year?
(b) Calculate the economic growth rate over the period. Discuss the policies that are available to the government to encourage long-term economic growth.
(c) Calculate the size of the GDP gap in 2019. Discuss the policies that are available to the government and the central bank to close the GDP gap.
(d) Consider the current COVID-19 crisis. Outline the development of the crisis in Singapore and detail the policies the government has undertaken in tackling the crisis. Given your understanding of the situation and economic theory and modeling, discuss the longer-term implications of this crisis for the Singapore economy.
(e) Given that average labor productivity can be calculated as real GDP calculate the number of employed workers ‘ average labor productivity for 2019. Discuss how the COVID-19 crisis is likely to impact average labor productivity and how this will impact long-run economic growth for the nation.
We provide 24*7 assignment writing services to NUS university scholars at an affordable price. Our expert assignment writer is available online at any time to give you the best support for Macroeconomics assignments. Avail our economics assignment help and score high.
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- INDIVIDUAL RESEARCH PROJECT: MERGERS AND THEIR IMPACT
- PSS388 End of Course Assessment January Semester 2025 SUSS : Integrated Public Safety And Security Management
- PSY205 Tutor-Marked Assignment 02 SUSS January 2025 : Social Psychology
- Math255 S1 Assignment-2025 SUSS : Mathematics for Computing
- BUS100 Tutor-Marked Assignment January 2025 SUSS : Business Skills And Management
- CSCXXX SUSS : New System Development Using Java : Soft Dev Pte Ltd Project
- Cloud Computing: Fundamentals, Networking, and Advanced Concepts
- COS364 Tutor-Marked Assignment January 2025 Sem SUSS : Interventions for At-Risk Youth
- FMT309 Tutor-Marked Assignment 01 SUSS January 2025 : Building Diagnostics
- HBC203 Tutor-Marked Assignment 01 January 2025 SUSS : Statistics and Data Analysis for the Social and Behavioural Sciences

