| University | Singapore University of Social Science (SUSS) |
| Subject | EAS201: Aerospace Propulsion |
SINGAPORE UNIVERSITY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES (SUSS) TMA – Page 1 of 10
EAS201
Aerospace Propulsion
_________________________________________
Tutor-Marked Assignment
January 2025
_________________________________________
TUTOR-MARKED ASSIGNMENT (TMA)
This assignment is worth 8% of the final mark for EAS201 Aerospace Propulsion.
There are 8 questions in this assignment. Answer all questions.
The cut-off date/time for submitting this assignment is 16 March 2025 (Sunday), 2200 hr.
Note to Students:
1. You are to include the following particulars in your submission: Course Code, Title of the TMA, SUSS PI No., Your Name, and Submission Date.
2. Pace your learning and workload. Instead of trying to complete this TMA at one go just before the cut-off date, you are advised to attempt the questions as soon as the chapter has been covered in class and after you have practised the respective tutorials.
3. Please use the same notation as the study guide or provide a legend if otherwise. Also, provide numerical answers to four (4) significant places.
Question 1 (10 marks) covering up to chapter 1
Question 1a(i)
Explain the term thermal efficiency of a turbojet engine. Discuss the engine parameter(s) that affect(s) its thermal efficiency.
(3 marks)
Question 1a(ii)
With the aid of appropriate thermodynamic relationship(s), explain how the thermal efficiency of a turbojet engine affects the engine fuel consumption efficiency.
(3 marks)
Question 1b
At sea-level static maximum power, a turbojet has the following performance measurements:
Intake airflow 125 kg/s
Forward velocity 720 km/h
Exhaust velocity 860 m/s
Assume the engine is ideal and that exhaust is fully expanded, and that fuel low heating value hPR = 42,800 kJ/kg. Ignoring the effect of fuel mass on engine thrust, compute the following parameters:
Question 1b(i)
Engine thrust.
(2 marks)
Question 1b(ii)
Engine propulsive efficiency
(2 marks)
Hire a Professional Essay & Assignment Writer for completing your Academic Assessments
Native Singapore Writers Team
- 100% Plagiarism-Free Essay
- Highest Satisfaction Rate
- Free Revision
- On-Time Delivery
Question 2 (10 marks) Chapter 3
Consider an ideal non-afterburning turbojet engine operating under the following conditions:
Altitude 18,000 feet
Ambient temperature T0 -20.6 ºC
Ambient pressure P0 50.6 kPa
Mach number M0 1.6
Intake air mass flow 𝑚̇ 0 125 kg/s
Engine exhaust velocity Ve 860 m/s
Fuel flow rate into the combustor 𝑚̇𝑓 3.5 kg/s
Low heating value of fuel hPR 42,800 kJ/ kg
Turbine exit total pressure Pt5 420 kPa
Exhaust gas static pressure P9 Fully expanded to ambient (=P0)
Ratio of specific heats of air γ 1.4
Gas constant of air R 287 J/(kg⋅K)
Taking into consideration the effects of fuel mass on engine thrust, evaluate the following:
Question 2a
Forward velocity in m/s.
(1 mark)
Question 2b
Net thrust.
(1 mark)
Question 2c
Specific thrust.
(1 mark)
Question 2d
Output power of the engine.
(1 mark)
Question 2e
Engine thermal efficiency.
(1 mark)
Question 2f
Propulsive efficiency.
(1 mark)
Question 2g
Overall efficiency.
(1 mark)
Question 2h
Thrust specific fuel consumption.
(1 mark)
Question 2i
Exhaust exit Mach number.
(2 marks)
Question 3 (10 marks) Chapter 3
Figure Q3 shows a schematic of an uninstalled unmixed turbofan engine, with station numbering according to SAE ARP 755A. 𝑚̇ 𝐶 and 𝑚̇ 𝐹 denote the air mass flowrates through the core engine and fan (bypass) section, respectively.
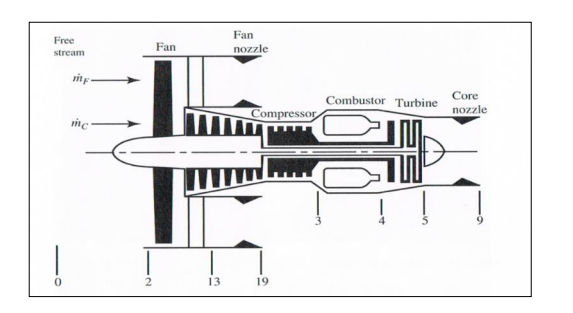
Figure Q3. Schematic of Twin Spool Turbofan Engine
Question 3a
Using the station numbering nomenclature, write down the expressions for the uninstalled thrust produced by the core engine 𝐹𝐶 and the fan section 𝐹𝐹, in terms of forward and exhaust velocities and the fuel mass flow. Assume that both the core engine and fan exhaust streams are fully expanded at their exits.
(2 marks)
Question 3b
Now, explain why the effect of fuel mass on the engine thrust can be reasonably neglected,
and hence show that the turbofan thrust can be derived as:
𝐹 =
𝑚̇ 0
𝑔𝑐
(1 + 𝛼)
[(𝑉9 − 𝑉0) + 𝛼(𝑉19 − 𝑉0)]
Where bypass ratio 𝛼 = 𝑚̇ 𝐹/𝑚̇ 𝐶
𝑚̇ 0 = total air mass flowrate through engine
𝑚̇𝑓 = fuel mass flowrate
Clearly show the steps of your derivation.
(8 marks)
Question 4 (10 marks) Chapter 3
A turbofan engine with bypass ratio of 3, consumes 0.5 kg/s of fuel when flying at 850 km/h.
Its total intake air mass flow is 100 kg/s. The exhaust velocities of the core engine and bypass duct are 480 m/s and 400 m/s, respectively and both exhaust streams exit at ambient pressure. Assume negligible losses and appropriate processes are isentropic.
Question 4a
Compute the engine fuel-air ratio.
(3 marks)
Question 4b
Evaluate the engine thrust. You may assume the fuel mass has a negligible effect on engine thrust.
(3 marks)
Question 4d
Determine the specific thrust of the engine.
(2 marks)
Question 4e
Analyse the thrust specific fuel consumption of the engine.
(2 marks)
Buy Custom Answer of This Assessment & Raise Your Grades
Question 5 (10 marks) Chapter 4
A turbojet engine with combustor exit temperature of 2000 K is to be designed for optimum operations in -56.3 ºC ambient temperature. Assume ideal conditions without losses. Take low heating value of jet fuel as 42,800 kJ/kg, and cp and γ for air as 1.004 kJ/(kg.K) and 1.4, respectively.
Question 5a
Compute the compressor pressure ratio such that the engine provides maximum specific thrust when operating at Mach 2.3 with afterburner.
(3 marks)
Question 5b
With the same compressor pressure ratio that you have determined in Question 5
a, the engine is also to cruise in the same ambient conditions but at a subsonic speed. Analyse the following performance of the engine when operating without afterburner:
Question 5b(i)
Evaluate the optimum subsonic Mach number such that the engine specific thrust is maximum.
(2 marks)
Question 5b(ii)
Determine the maximum specific thrust.
(3 marks)
Question 5a(ii)
Solve the subsonic cruise thrust specific fuel consumption.
(2 marks)
Question 6 (10 marks) Chapter 4
Perform a parametric cycle analysis of an ideal turbojet engine with the following input.
Assume constant values of γ = 1.4 and R =287 J/(kg.K) for air.
Flight conditions:
Altitude 35,000 feet
Ambient temperature 219 K
Ambient pressure 23.8 kPa
Flight Mach number 1.4
Engine design parameters:
Type of compressor Axial-flow, dual spool
Overall compressor pressure ratio 22
Combustor exit temperature 1900 K
Question 6a
For the turbojet engine, analyse the following values:
Question 6a(i)
Compressor exit total temperature Tt3.
(1 mark)
Question 6a(ii)
Burner total temperature ratio τb (Note: this ratio is different from burner enthalpy ratio τλ).
(1 mark)
Question 6a(iii)
Turbine total pressure ratio πt.
(2 marks)
Question 6a(iv)
Exhaust Mach number M9.
(3 marks)
Question 6b
Beginning from station 0 through station 9, illustrate by means of a H-K diagram, the dimensionless energy levels of the air as it passes through the above engine. Indicate the key values on the diagram.
(3 marks)
Question 7 (10 marks) Chapter 5
During bench testing (assume no intake loss), a geared turbofan engine has the following test
data:
Ambient temperature T0 25 ºC
Ambient pressure P0 101 kPa
Fan exit total temperature Tt13 95 ºC
Fan exit total pressure Pt13 198 kPa
Outer fan air mass flow 𝑚̇ 𝐹 220 kg/s
Core engine air mass flow 𝑚̇ 𝐶 30 kg/s
For air, assume R = 287 kJ/(kg K), γc = 1.4.
Question 7a(i)
Compute the bypass ratio of the engine.
(1 mark)
Question 7a(ii)
Evaluate the isentropic efficiency and the polytropic efficiency of the fan.
(4 marks)
Question 7a(iii)
Determine the outer fan power imparted to the bypass air.
(2 marks)
Question 7b
The fan gear ratio is then increased so that the fan exit total pressure is raised to 210 kPa in the same ambient condition.
Question 7b(i)
Evaluate the new fan exit total temperature. State the assumption(s) for your evaluation to be valid.
(2 marks)
Question 7b(ii)
Analyse the new fan isentropic efficiency.
(1 mark)
Question 8 (30 marks) Chapter 6-7
A non-afterburning turbojet with a single-spool axial compressor has the following reference
data.
Altitude 35,000 ft
Ambient temperature T0 = 219 K
Ambient pressure P0 = 23.8 kPa
Flight Mach Number M0 = 1.4
Maximum intake diffuser pressure recovery πdmax = 0.96
Intake ram pressure recovery efficiency:
– for M0 ≤ 1 𝜂𝑟 = 1
– for 1 < 𝑀0 < 5 𝜂𝑟 = 1 − 0.075(M0 − 1)
1.35
Compressor pressure ratio πc = 22
Burner pressure ratio πb = 0.98
Nozzle pressure ratio πn = 0.96
Exhaust pressure ratio P0/P9 = 1
Turbine inlet temperature Tt4 = 1900 K
Compressor polytropic efficiency ec = 0.90
Turbine polytropic efficiency et = 0.91
Burner efficiency ηb = 0.95
Mechanical efficiency ηm = 0.98
Ratio of specific heats (upstream of burner) γc = 1.4
Ratio of specific heats (downstream of burner) γt = 1.32
Specific heat at constant pressure for air cpc=1.004 kJ/(kg K)
Specific heat at constant pressure for combustion products cpt =1.239 kJ/(kg K)
Low heating value of fuel hPR = 42,800 kJ/ kg
(a) Perform the parametric cycle analysis to obtain single point output. (Note: It is advisable to write down all relevant temperature and pressure ratios as you calculate them, as you will likely have to use them again subsequently.)
(i) Compute the compressor total temperature ratio.
(1 mark)
(ii) Determine the compressor efficiency.
(1 mark)
(iii) Calculate the fuel-air ratio
(3 marks)
(iv) Evaluate the turbine pressure ratio.
(3 marks)
(v) Determine the exhaust nozzle exit Mach number M9.
(5 marks)
(vi) Compute the exhaust velocity ratio 𝑉9
𝑎0
(3 marks)
(vii) Analyse the engine specific thrust.
(3 marks)
(viii) Determine the thrust specific fuel consumption.
(1 mark)
(b) Discuss the typical input and output parameters in the parametric analysis of a turbojet engine. Hence, explain the difference between parametric cycle analysis and engine performance analysis (or off-design analysis).
(3 marks)
(c) Perform an off-design analysis on the reference engine, with its burner exit temperature reduced to 1460K as it flies at Mach 0.85 in the same ambient conditions:
(i) Compute the combustor enthalpy ratio.
(1 mark)
(ii) Analyse the off-design compressor pressure ratio. State your assumptions for this analysis to be valid.
(5 marks)
(iii) Determine the new fuel-air ratio.
(1 mark)
Stuck with a lot of homework assignments and feeling stressed ? Take professional academic assistance & Get 100% Plagiarism free papers
Looking for Plagiarism free Answers for your college/ university Assignments.
- ISIT332 Business Process Management Individual Assignment 1
- A3740C Complementary and Alternative Medicine Graded Assignment
- A2859C Pharmacotherapeutics I Graded Assignment Brief 2026
- A3750C Dietary Supplements Graded Assignment Individual Report 2026
- Introduction to Accounting Assessment Questions | SMU
- B2079C Job and Labour Market Analysis Coursework Assessment AY2025 Term 4
- B2089C Career Development and Counselling Coursework Assessment AY2025
- PSB501EN Mechanical Engineering Systems Assessment Brief | CU
- 303SD Structural Steel Design Project Brief Report SEM 2 | Ngee Ann Polytechnic
- Security Risk Management Individual Project Assignment | SIT

